Appearance#
Appearance is the parent-class of Background and Costume
Backgrounds and Costumes are also Appearances - All objects of these types inherit all attributes and methods who are defined in this class.
Appearance#
- class miniworlds.appearances.appearance.Appearance(*args, **kwargs)[Quellcode]#
Basisklasse von Actorkostümen und Welt-Hintergründen
Die Klasse enthält alle Methoden und Attribute, um Bilder der Objekte anzuzeigen und zu animieren, Text auf den Bildern darzustellen oder Overlays anzuzeigen.
Öffentliche Datenattribute:
If True, the image is tiled over the background.
If True, costume will be rotated with token direction
Flips the costume or background.
Wenn True, wird das Bild unter Beibehaltung des Seitenverhältnisses hochskaliert.
Skaliert das Token auf die Größe des übergeordneten Elements, ohne das Seitenverhältnis beizubehalten.
Wenn True, wird das Bild vor der Drehung entsprechend der Ausrichtung des übergeordneten Elements gedreht.
Defines a colored layer.
Defines a transparency.
transparent, 255: visible If value < 1, it will be multiplied with 255.
If True, the costume will be animated.
->Füllfarbe anzeigen
see border color
border color of actor
Die Randgröße des Actors.
Führt alle Aktionen in der Bildpipeline aus
In Unterklassen Kostüm und Hintergrund implementiert
image_managerPublic Methods:
__init__()set_image(source)Legt das angezeigte Bild des Kostüms/Hintergrunds auf den ausgewählten Index fest
set_mode(**kwargs)set_animated(value)flip(value)add_image(source)Adds an image to the appearance
add_images(sources)Adds multiple images to background/costume.
animate([loop])Animates the costume
the method is overwritten in subclasses costume and appearance
Create an array from costume or background.
from_array(arr)Create a background or costume from array.
fill(value)Set default fill color for borders and lines
set_filled(value)get_color(position)get_rect()draw(source, position, width, height)draw_on_image(path, position, width, height)draw_color_on_image(color, position, width, ...)__str__()Return str(self).
If dirty, the image will be reloaded.
update()Loads the next image, called 1/frame
register(method)Register method for decorator.
draw_shape_append(shape, arguments)draw_shape_set(shape, arguments)draw_image_append(surface, rect)draw_image_set(surface, rect)set_dirty([value, status])In Unterklassen Kostüm und Hintergrund implementiert
Private Data Attributes:
_abc_implPrivate Methods:
_set_defaults(**kwargs)_set_font(font, font_size)_set_animation_speed(value)_set_textured(value)bool: If True, the image is tiled over the background.
_set_rotatable(value)If set to True, costume will be rotated with actor direction
_set_centered(value)_set_flipped(value)Flips the costume or background.
_set_filled(value)Flips the costume or background.
_set_scaled(value)Setzt den Actor auf die Eltern-Größe ohne das Seitenverhältnis beizubehalten.
_set_upscaled(value)Wenn auf Wahr gesetzt, wird das Bild unter Beibehaltung des Seitenverhältnisses hochskaliert.
_set_scaled_to_width(value)_set_scaled_to_height(value)_set_image(source)Legt das angezeigte Bild des Kostüms/Hintergrunds auf den ausgewählten Index fest
_before_transformation_pipeline()Aufgerufen in
get_image, wenn das Bild “dirty” ist (z. B. Größe, Drehung, ._after_transformation_pipeline()Aufgerufen in
get_image, wenn das Bild “dirty” ist (z. B. Größe, Drehung, ._load_image()Loads the image,
_update_draw_shape()_inner_shape()Returns inner shape of costume
_outer_shape()Returns outer shape of costume
_inner_shape_arguments()def setGets arguments for inner shape
_outer_shape_arguments()Gets arguments for outer shape
- LOAD_NEW_IMAGE = 2#
- RELOAD_ACTUAL_IMAGE = 1#
- add_image(source)[Quellcode]#
Adds an image to the appearance
- Rückgabetyp:
- Rückgabe:
Index des erstellten Bildes.
- add_images(sources)[Quellcode]#
Adds multiple images to background/costume.
Jede Source im Source-Parameter muss ein gültiger Parameter für :py:attr:
Appearance.cimagesein
- after_animation()[Quellcode]#
the method is overwritten in subclasses costume and appearance
Beispiele
Der Actor wird nach der Animation entfernt - Dies kann für Explosionen verwendet werden.
from miniworlds import * world = World() actor = Actor() costume = actor.add_costume("images/1.png") costume.add_image("images/2.png") costume.animate() @costume.register def after_animation(self): self.parent.remove() world.run()
- after_init()[Quellcode]#
- property alpha#
transparent, 255: visible If value < 1, it will be multiplied with 255.
Beispiele
from miniworlds import * world = World(800,400) t = Actor((600,250)) t.add_costume("images/alien1.png") t.costume.alpha = 50 t.width = 40 t.border = 1 world.run()

- Typ:
definiert die Transparenz des Actors
- Typ:
0
- animate(loop=False)[Quellcode]#
Animates the costume
- Parameter:
loop – Wenn loop = True ist, wird die Animation als Schleife verarbeitet. (Sie können dies mit self.loop stoppen)
from miniworlds import * world = World(80,40) robo = Actor() robo.costume.add_images(["images/1.png"]) robo.costume.add_images(["images/2.png","images/3.png","images/4.png"]) robo.costume.animation_speed = 20 robo.costume.is_animated = True world.run()
- property animation_speed#
- property border#
Die Randgröße des Actors.
Der Wert ist 0, wenn der Actor keinen Rand hat
- Rückgabe:
int
- Rückgabetyp:
_type_
- property border_color#
border color of actor
- property color#
->Füllfarbe anzeigen
- property coloring#
Defines a colored layer.
coloringkann True oder false sein. Die Farbe wird durch das Attributappearance.colordefiniert.
- counter = 0#
- property dirty#
- draw(source, position, width, height)[Quellcode]#
- draw_color_on_image(color, position, width, height)[Quellcode]#
- draw_image_append(surface, rect)[Quellcode]#
- draw_image_set(surface, rect)[Quellcode]#
- draw_on_image(path, position, width, height)[Quellcode]#
- draw_shape_append(shape, arguments)[Quellcode]#
- draw_shape_set(shape, arguments)[Quellcode]#
- fill(value)[Quellcode]#
Set default fill color for borders and lines
- property fill_color#
- flip(value)[Quellcode]#
- property font_size#
- from_array(arr)[Quellcode]#
Erstellen Sie einen Hintergrund oder ein Kostüm aus einem Array. Das Array muss ein
numpy.ndarraysein, das mit.to_colors_arrayerstellt werden kannBeispiele
Konvertiere grauen Standardhintergrund in einen Farbverlauf
from miniworlds import * world = World() arr = world.background.to_colors_array() for x in range(len(arr)): for y in range(len(arr[0])): arr[x][y][0] = ((x +1 ) / world.width) * 255 arr[x][y][1] = ((y +1 ) /world.width) * 255 world.background.from_array(arr) world.run() world.background.from_array(arr) world.run()
Ausgabe:
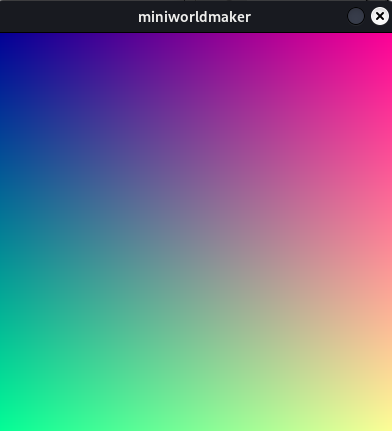
- get_color(position)[Quellcode]#
- get_image()[Quellcode]#
Wenn verschmutzt, wird das Bild neu geladen. Die Bildpipeline wird verarbeitet, definiert durch “set_dirty”
- abstract get_manager()[Quellcode]#
In Unterklassen Kostüm und Hintergrund implementiert
- get_modes()[Quellcode]#
- get_rect()[Quellcode]#
- property image: Surface#
Führt alle Aktionen in der Bildpipeline aus
- property images#
- property is_animated#
If True, the costume will be animated.
from miniworlds import * world = World(80,40) robo = Actor() robo.costume.add_images(["images/1.png"]) robo.costume.add_images(["images/2.png","images/3.png","images/4.png"]) robo.costume.animation_speed = 20 robo.costume.is_animated = True world.run()
- property is_centered#
- property is_filled#
- property is_flipped#
Spiegelt das Kostüm oder den Hintergrund. Das Bild wird über die y-Achse des Kostüms/Hintergrunds gespiegelt.
Beispiele
Flippt Actor:
from miniworlds import * world = World() token = Token() token.add_costume("images/alien1.png") token.height= 400 token.width = 100 token.is_rotatable = False @token.register def act(self): if self.world.frame % 100 == 0: if self.costume.is_flipped: self.costume.is_flipped = False else: self.costume.is_flipped = True world.run()


- property is_rotatable#
If True, costume will be rotated with token direction
- property is_scaled#
Skaliert das Token auf die Größe des übergeordneten Elements, ohne das Seitenverhältnis beizubehalten.
- property is_scaled_to_height#
- property is_scaled_to_width#
- property is_textured#
If True, the image is tiled over the background.
Beispiele
Texturiere das Brett mit dem gegebenen Bild:
from miniworlds import * world = World() background = world.add_background("images/stone.png") background.is_textured = True world.run()

Texturgröße festlegen
from miniworlds import * world = World() background = world.add_background("images/stone.png") background.is_textured = True background.texture_size = (15,15) world.run()

- Typ:
- property is_upscaled#
Wenn True, wird das Bild unter Beibehaltung des Seitenverhältnisses hochskaliert.
- property orientation#
Wenn True, wird das Bild vor der Drehung entsprechend der Ausrichtung des übergeordneten Elements gedreht.
Beispiele
Beide Actor steigen auf. Das Bild von t2 ist korrekt ausgerichtet. t1 schaut in die falsche Richtung.
from miniworlds import * world = TiledWorld() t1 = Actor((4,4)) t1.add_costume("images/player.png") t1.move() t2 = Actor((4,5)) t2.add_costume("images/player.png") t2.orientation = - 90 t2.move() @t1.register def act(self): self.move() @t2.register def act(self): self.move() world.run()

- Typ:
- register(method)[Quellcode]#
Registriere Methode für Dekorator. Registriert Methode für Actor oder Hintergrund.
- remove_last_image()[Quellcode]#
- set_animated(value)[Quellcode]#
- set_dirty(value='all', status=1)[Quellcode]#
- set_filled(value)[Quellcode]#
- set_image(source)[Quellcode]#
Legt das angezeigte Bild des Kostüms/Hintergrunds auf den ausgewählten Index fest
- Rückgabetyp:
- Parameter:
source – Der Bildindex oder ein Bild.
- Rückgabe:
Wahr, wenn der Bildindex existiert
Beispiele
Fügen Sie zwei Bilder zum Hintergrund hinzu und wechseln Sie zu Bild 2
from miniworlds import * world = World() background = world.add_background("images/1.png") background.add_image("images/2.png") background.set_image(1) world.run()
- set_mode(**kwargs)[Quellcode]#
- property stroke_color#
see border color
- property texture_size#
- to_colors_array()[Quellcode]#
Erstelle ein Array aus Kostüm oder Hintergrund. Das Array kann mit
.from_arrayin ein Appearance umgeschrieben werdenExamples: :rtype:
ndarrayEin Hintergrundbild in Graustufen umwandeln
from miniworlds import * world = World(600,400) world.add_background("images/sunflower.jpg") arr = world.background.to_colors_array() def brightness(r, g, b): return (int(r) + int(g) + int(b)) / 3 for x in range(len(arr)): for y in range(len(arr[0])): arr[x][y] = brightness(arr[x][y][0], arr[x][y][1], arr[x][y][2]) world.background.from_array(arr) world.run()
Ausgabe:

- property transparency#
Defines a transparency.
Wenn
transparencyTrueist, wird der Transparenzwert durch das Attributappearance.alphadefiniert
- update()[Quellcode]#
Loads the next image, called 1/frame